互联网非常复杂,其复杂性很类似高速公路系统。但是,数据想方设法找到它。 NAT 是一种帮助不丢失数据的工具。下面来看看它是如何工作的以及其主要目的是什么。
什么是 NAT?
NAT(或网络地址转换)是将多个本地 IP 地址映射到公共 IP 地址的过程。它是数据包通过路由设备时,修改数据包的 IP 标头中的网络地址数据来完成的。
此过程使唯一的 IP 地址能够代表整个计算机组。因为单个 IP 地址可以代表整个私有网络,所以,在IPv4 地址耗尽后,被广泛用于节省在线地址空间。
NAT 是如何工作的?
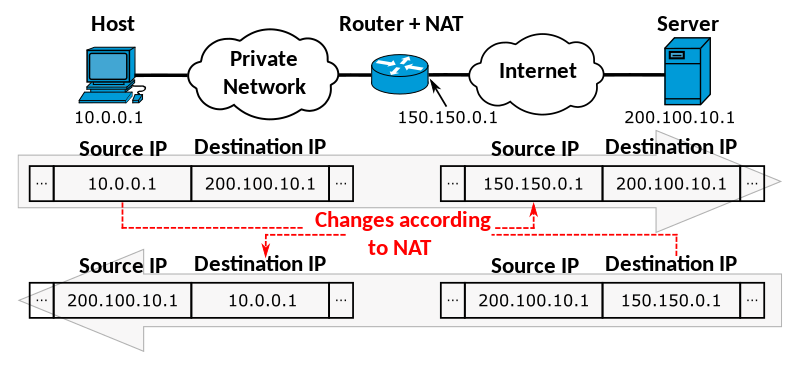
NAT 将您的私有 IP 地址转换为公共 IP 地址。假设您在 Google 上搜索附近的食品店。该请求从您的笔记本电脑发送到路由器,然后发送到网络。但是,更改发生在路由器内。此设备将您的私有 IP 地址更改为公共 IP 地址。然后请求的接收者识别公共地址并将信息发回给您。这样就建立了连接。
因此 NAT 允许单个设备(例如路由器)成为专用网络和公共网络之间的代理。那么单个网络的设备可以用万维网上的单个 IP 来表示。
从这个意义上说,NAT 让人想起在一家大公司指挥、阻止和发送电话的接待员。NAT 充当您的网络和外部网络之间的过滤器,它处理所有请求而不泄露您的私有 IP 地址。
NAT 的类型
以下是几种主要的 NAT 类型:
- 静态 NAT。这种类型的 NAT 始终使用相同的公共 IP 地址。当您的设备需要从外部网络访问时,它特别有用。
- 动态 NAT。在这种情况下,NAT 每次都使用不同的公共 IP 地址。它从其 IP 地址池中选择地址。
- 重载或 PAT(端口地址转换)。这是一种动态 NAT 形式,它通过使用不同的端口将多个未注册的 IP 地址映射到一个已注册的 IP 地址。这种类型的 NAT 在希望其员工在网络管理员的监督下使用单个 IP 地址的组织中很受欢迎。它还具有成本效益,因为许多用户使用单个 IP 连接到互联网。
- 重叠。当您的内部网络上使用的注册 IP 地址也用于多个内部网络时,就会发生重叠 NAT。当组织希望很少的网络在不重新寻址其设备的情况下进行通信时使用它。
为什么使用 NAT?
以下是使用 NAT 的几个原因:
- 它有助于节省 IP 地址。如果没有 NAT,互联网最终将没有足够的 IP 地址,我们的数据将无法在网络上导航。
- 它增强了您的安全性。NAT 创建内部和外部网络之间的边界。基本上,除非它发起联系,否则没有人可以连接到您的计算机。没有外部代理可以使用您的 IP 地址来拦截您的设备或网络。
- 更轻松的网络管理。NAT 允许将 Web 和 FTP 服务器移动到其他主机,并且可以更轻松地在内部网络上进行更改。








